Greenhouse Gases such as carbon dioxide is the primary cause for the Greenhouse Effect The major contributors to the greenhouses gases are factories, automobiles, deforestation , etc The increased number of factories and automobiles increases the amount of these gases Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, andTwo identical glass jars 4 cups cold water 10 ice cubes

Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
What is greenhouse gas and its effect
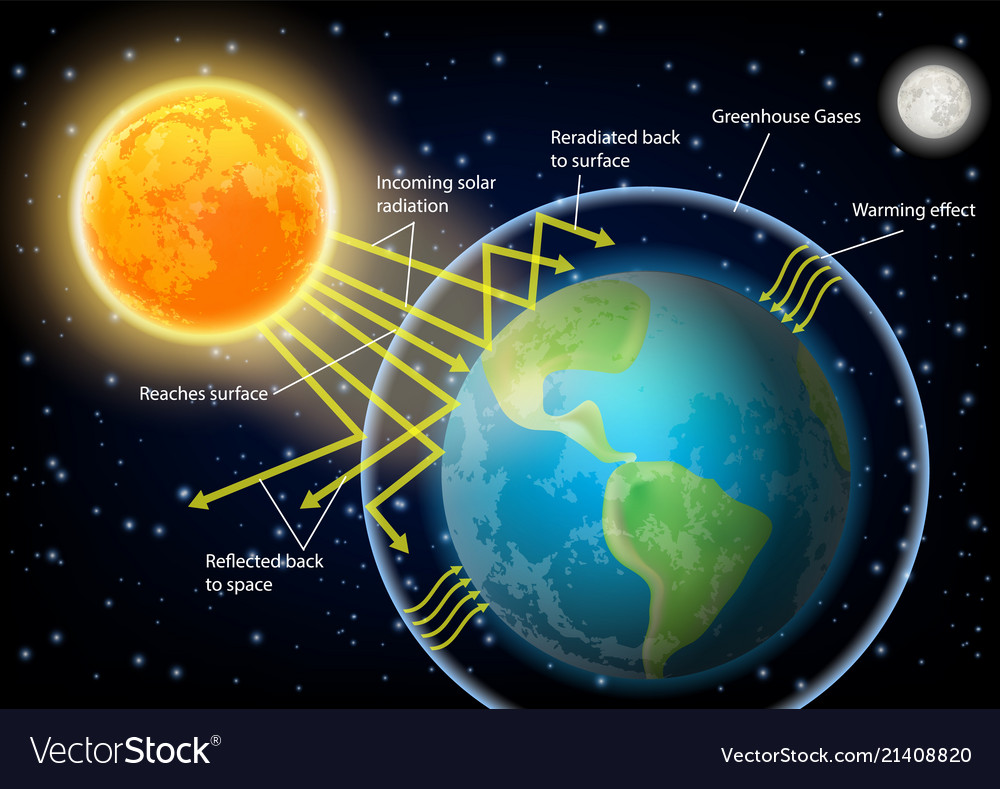
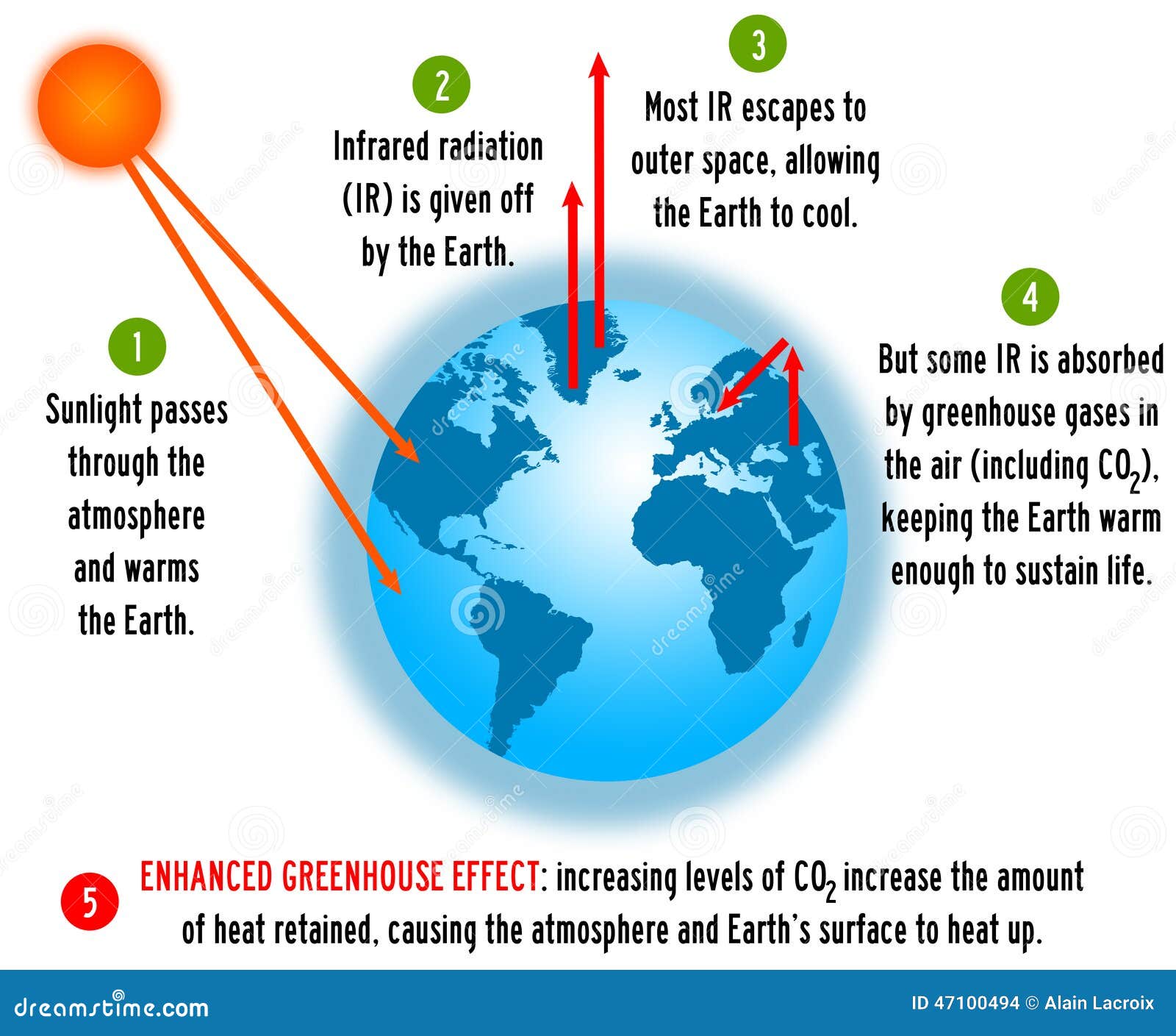
What is greenhouse gas and its effect-This diagram explains to us about the greenhouse effect Basically what greenhouse effect is, is the sun, which emits mostly long radiation and shortwave radiation, all this radiation comes in in the morning or during daytime without any problem The atmosphere, which has various kinds of gases like oxygen, nitrogen, little bit of carbon dioxide, et cetera, these radiations basically pass throughThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
This is known as the greenhouse effect Certain gases have been increasing in concentration in the atmosphere on a timeline concurrent with increasing global temperature Teacher Activity How do greenhouse gases Show students the following diagram that is a part of their worksheet Have them attempt to place the labels on the appropriate Amplifying the greenhouse effect Like other gases in the atmosphere, including oxygen and nitrogen, greenhouse gases are largely transparent to incoming sunlight Unlike those more abundant gases though, greenhouse gases are not transparent to heat (longwave infrared radiation) The sunwarmed surface of Earth radiates heat day and nightGreenhouse gases diagrams • Where do Greenhouse Gases Come From handouts • Greenhouse Gas Emissions Diagram handouts • Colored pencils National Science Education Standards D1h The atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases that include water vapor
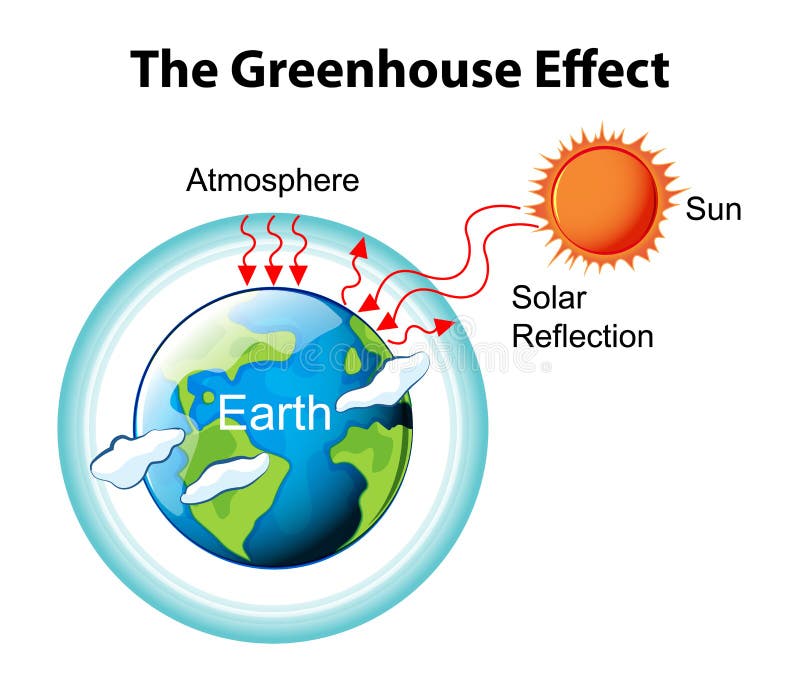
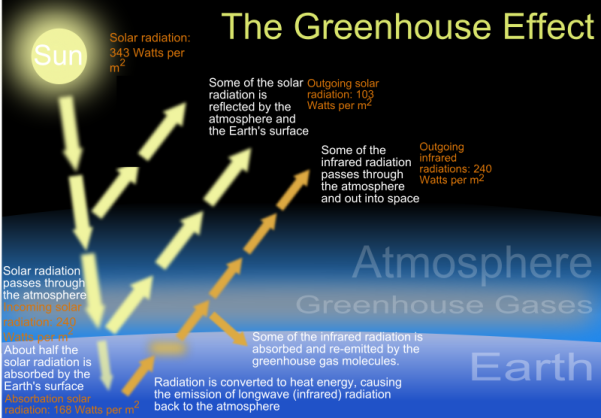
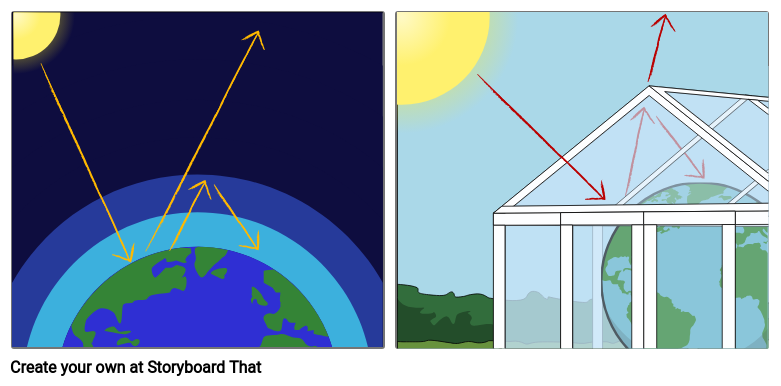
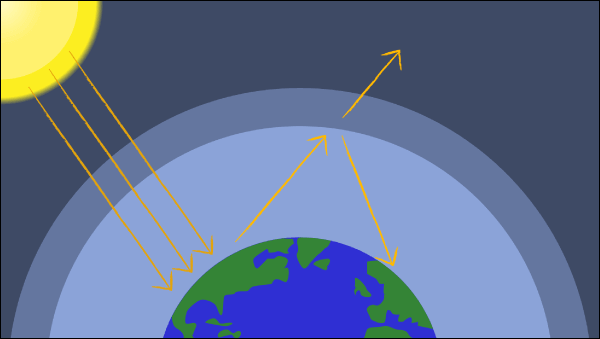
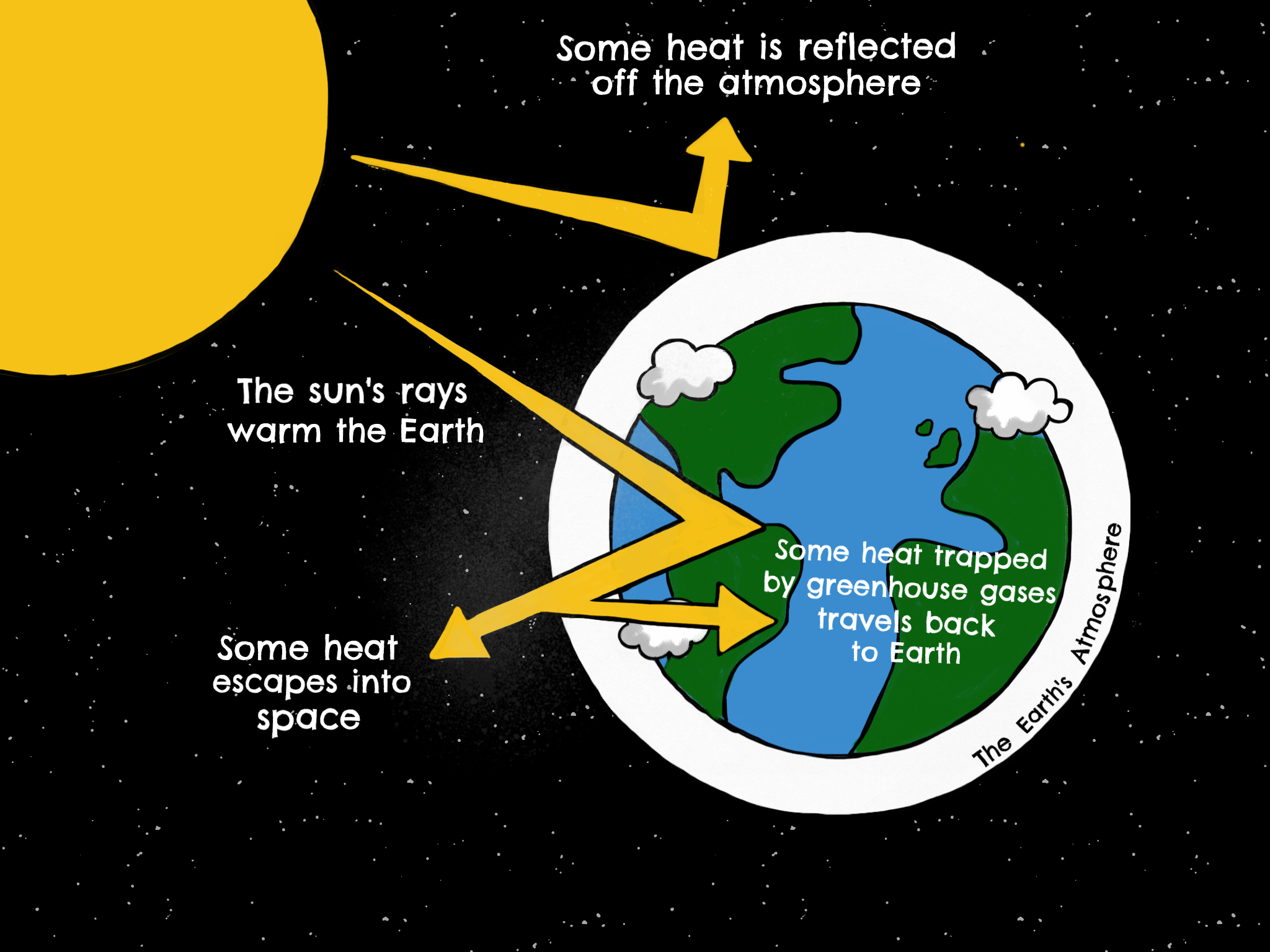
Greenhouse effect Step 1 Solar radiation reaches the Earth's atmosphere some of this is reflected back into space Step 2 The rest of the sun's energy is absorbed by the land and the oceans, heating the Earth Step 3 Heat radiates from Earth towards spaceThe Natural Greenhouse Effect Just as the major atmospheric gases (oxygen and nitrogen) are transparent to incoming sunlight, they are also transparent to outgoing heat energy However, water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and other trace gases are "opaque" to many wavelengths of heat energy, and so trap that heat in the atmosphereThe "Greenhouse Effect" A greenhouse is a building made of glass that allows sunlight to enter but traps heat inside, so the building stays warm even when it's cold outside Because gases in the Earth's atmosphere also let in light but trap heat, many people call this phenomenon the "greenhouse effect" The greenhouse effect works
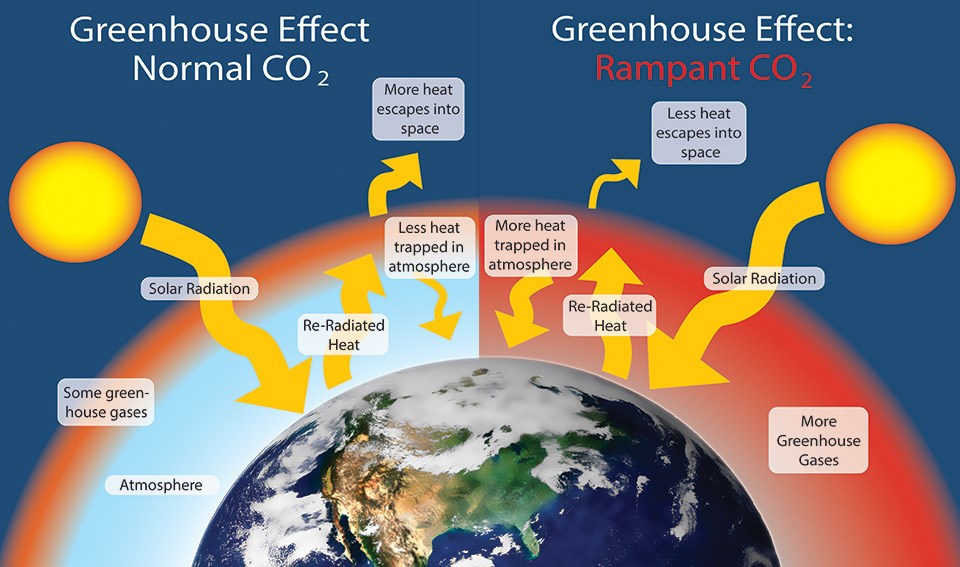
Landfill gas (LFG) is a natural byproduct of the decomposition of organic material in landfills LFG is composed of roughly 50 percent methane (the primary component of natural gas), 50 percent carbon dioxide (CO 2) and a small amount of nonmethane organic compounds Methane is a potent greenhouse gas 28 to 36 times more effective than CO 2 atThe effect of increased greenhouse gas concentrations The natural greenhouse effect The greenhouse effect is a warming of the earth's surface and lower atmosphere caused by substances such as carbon dioxide and water vapour which let the sun's energy through to the ground but impede the passage of energy from the earth back into spaceGreenhouse effect, a warming of Earth 's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The greenhouse effect on Earth




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
The diagram gives more details about this process, called the greenhouse effect How the greenhouse effect works Electromagnetic radiation at most wavelengths passes through the Earth's atmosphereA greenhouse gas is a gas which reflects radiation that the Earth emits, and stops it from being lost into space This makes the Earth hotter than it would be without greenhouse gases This is called the " greenhouse effect " A diagram of the greenhouse effect Energy flows between space, the atmosphere, and Earth's surface Tyndall soon established that carbon dioxide and water vapour were among the gases that absorbed heat, and also that they radiated heat, the physical basis of the greenhouse effect In making these discoveries, Tyndall set the foundation for our modern understanding of the greenhouse effect, climate change, meteorology, and weather




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



Untitled Document
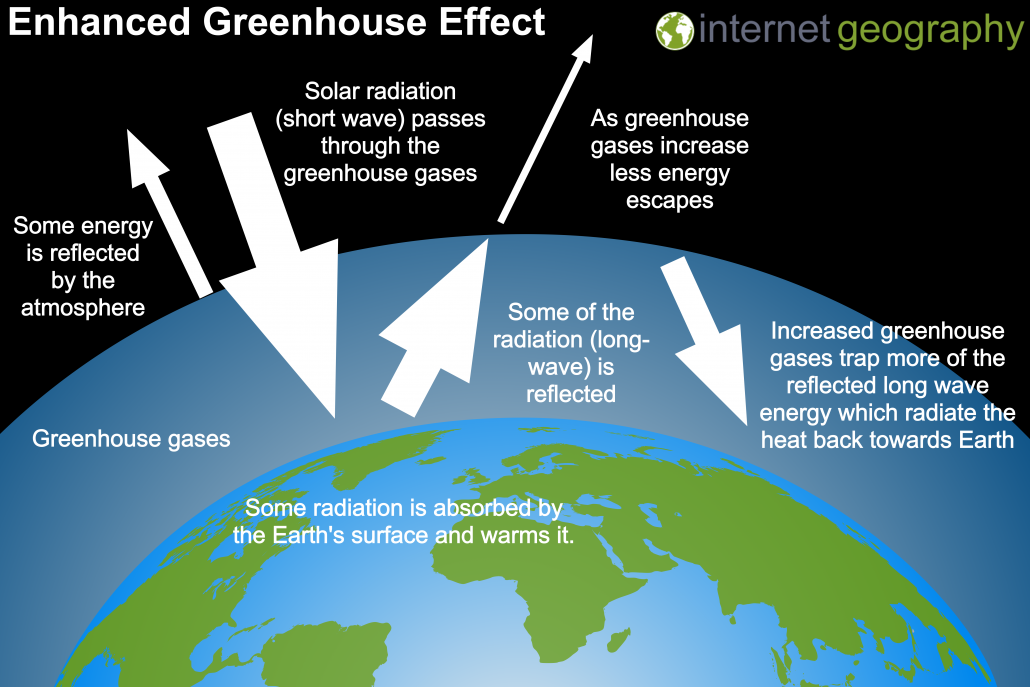
Without some greenhouse gases and the Greenhouse Effect, Earth's temperature would be close to 18°C 5 The Earth naturally takes up about half the carbon dioxide produced by humans 6 Plants, soil, and water take up carbon dioxide (CO 2) If this is stored for a long time, this is known Greenhouse gases also increase the rate at which the atmosphere can absorb shortwave radiation from the Sun, but this has a much weaker effect on global temperatures The CO 2 released from the burning of fossil fuels is accumulating as an insulating blanket around the Earth, trapping more of the Sun's heat in our atmosphereThe common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is air By volume, dry air contains 7809% nitrogen, 95% oxygen, 093% argon, 0039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% Although air content and atmospheric pressure vary




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts
Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not The greenhouse effect is the process thanks to which Earth has a higher temperature than it would have without it The gases that radiate heat also known as greenhouse gases absorb the energy radiated out by the Earth and reflect a part of it back to EarthImportant Greenhouse Gases (concentrations in parts per million volume) water vapor 0140,000 carbon dioxide 370 methane 17 nitrous oxide 03 ozone 001 chlorofluorocarbons ~ A greenhouse gas is defined as a gas that absorbs significantly the radiation emitted by the Earth and its atmosphere (Infrared, IR, or longwave radiation)



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




Schematic Of Greenhouse Gas Effect 8 Download Scientific Diagram
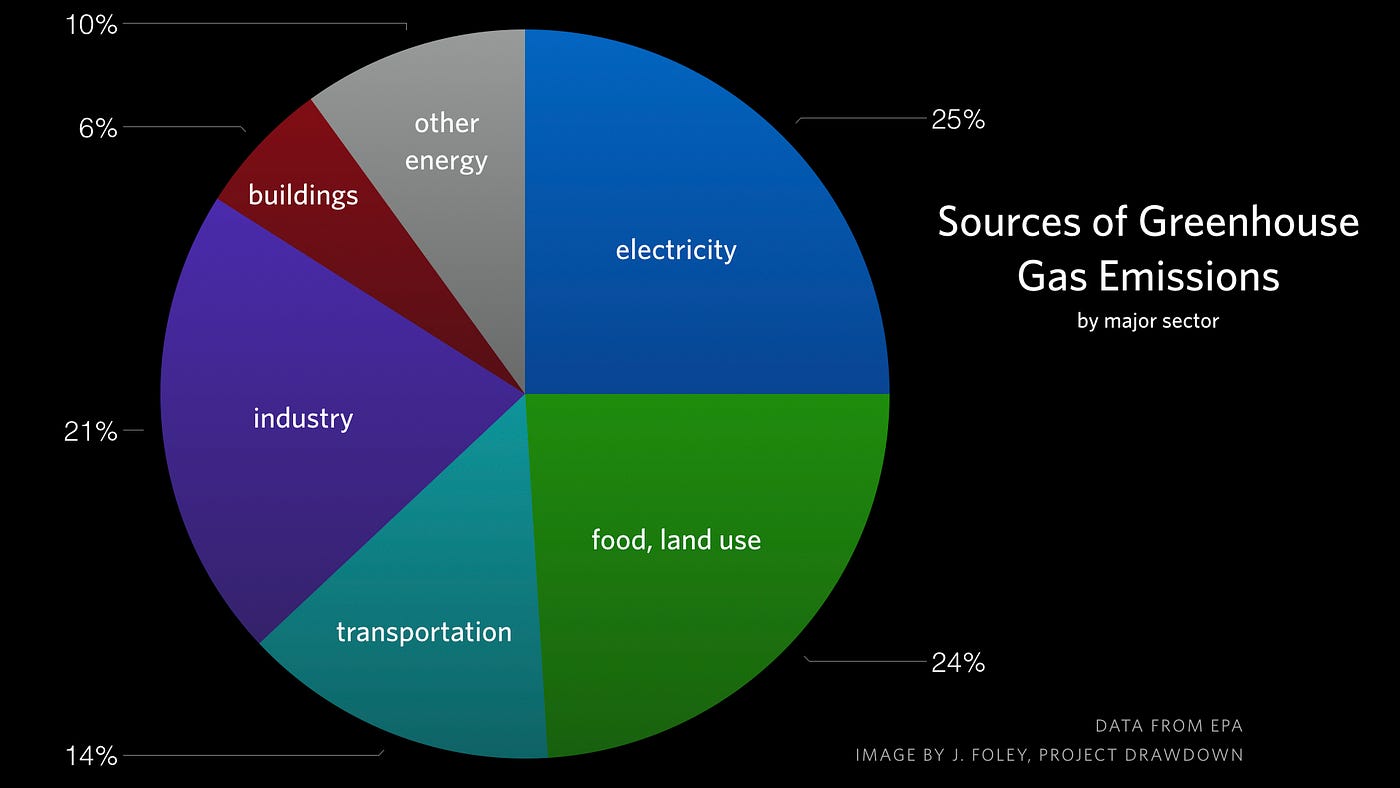
Greenhouse Gas Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 2530% Futtsu Thermal Power Station near Tokyo Generating electricity and heat by burning fossil fuels like coal, natural gas and oil produces more greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions than any human activity, accounting for at least one quarter of all global emissions The greenhouse effect works much the same way on Earth Gases in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, trap heat similar to the glass roof of a greenhouse These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases During the day, the Sun shines through the atmosphere Earth's surface warms up in the sunlight The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which the specific gases in the atmosphere of the Earth trap heat from the sun (see The Greenhouse Effect Diagram attachment) Typically, our atmosphere absorbs just the




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
The greenhouse effect plays a significant role in Earth's energy budgetWith the natural greenhouse effect, the energy budget is balanced as thermal radiation is reradiated towards the ground, trapping thermal energy and warming the Earth However, with the greenhouse effect being enhanced by humans, the energy budget of the Earth is shifted to an imbalanceGreenhouse gases from human activities are the most significant driver of observed climate change since the mid th century 1 The indicators in this chapter characterize emissions of the major greenhouse gases resulting from human activities, the concentrations of these gases in the atmosphere, and how emissions and concentrations have changed over timeThe diagram outlines how the greenhouse effect works Sunlight passes through the Earth's atmosphere The ground warms up and heat is emitted from the Earth's surface Some heat escapes into space




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some ofA greenhouse gas (GHG or GhG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy within the thermal infrared range, causing the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H 2 O), carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), and ozone (O 3) Without greenhouse gases, the average temperature of Earth's surface would The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to the surface of the Earth by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around the Earth, which keeps it toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases arise naturally, and are part of




Greenhouse Effect Sankey Diagrams




Greenhouse Gases Easy Drawing Novocom Top
The greenhouse effect is a warming of Earth's surface and the air above it It is caused by gases in the air that trap energy from the Sun These heattrapping gases are called greenhouse gases The most common greenhouse gases are water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane Without the greenhouse effect, Earth would be too cold for life to exist Five Major Greenhouse Gases The most significant gases that cause global warming via the greenhouse effect are the following Carbon Dioxide Accounting for about 76 percent of global humancausedThe greenhouse effect has kept the Earth's average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve Over the past several millennia the average Earth temperature has been about 15 °C (59 °F) The figure below illustrates how greenhouse gases keep the Earth warmer than it would be




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram



A Simplified Diagram Illustrating The Effect Of Greenhouse Gases On Download Scientific Diagram
Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, which makes the Earth warmer People are adding several types of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere, and each gas's effect on climate change depends on three main factorsThe gases formed by the burning, such as carbon dioxide, are building up in the atmosphere They act like greenhouse glass The result, experts believe, is that the Earth heating up and undergoing global warming How can you show the greenhouse effect?Sulfur hexafluoride (SF 6) is an extremely potent greenhouse gas SF 6 is very persistent, with an atmospheric lifetime of more than a thousand years Thus, a relatively small amount of SF 6 can have a significant longterm impact on global climate change SF 6 is humanmade, and the primary user of SF 6 is the electric power industry Because of its inertness and dielectric properties, it is



Http Gzscienceclassonline Weebly Com Uploads 1 1 3 6 The Greenhouse Effect Year 9 Gz Pdf



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
That approach in effect makes carbon dioxide, CO 2, the prevailing "currency" of greenhouse gases and global warming Let's consider the principal GHGs one at a time, starting with water vapor, the most abundant greenhouse gas in the atmosphere according to NOAA's National Climatic Data Center (NCDC)Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gasesTo the right is a diagram (also from NOAA, ESRL, the same source as the table above) which illustrates the greenhouse effect Since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution (round about the late 1700's), the concentration of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere has rocketed by an estimate of 30%, most significantly carbon dioxide




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock
The greenhouse effect is the process by which radiation from a planet's atmosphere warms the planet's surface to a temperature above what it would be without this atmosphere Radiatively active gases in a planet's atmosphere radiate energy in all directions Part of this radiation is directed towards the surface, thus warming it The intensity of downward radiation – that is, the strength of the greenhouse effect – depends on the amount of greenhouse gases 247 greenhouse effect diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royaltyfree See greenhouse effect diagram stock video clips of 3 global warming, sun earth diagram energy global problems effects global warming greenhouse effect global waste management greenhouse effect vector global warming icons greenhouse gas effect Graphic A simplified animation of the greenhouse effect Perhaps the most impressive of cloud formations, cumulonimbus (from the Latin for "pile" and "rain cloud") clouds form due to vigorous convection (rising and overturning) of warm, moist and unstable air




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet



1
The Greenhouse Effect Goal Students will learn how greenhouse gases temporarily trap heat within Earth's atmosphere, warming our planet via the greenhouse effect Activity Students explore the greenhouse effect through computer simulations and then dive deeper learning how the greenhouse effect works via readings and videos onlineGreenhouse effect Noun phenomenon where gases allow sunlight to enter Earth's atmosphere but make it difficult for heat to escape greenhouse gas Noun gas in the atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and ozone, that absorbs solar heat reflected by the surface of the Earth, warming the atmosphere solar energyWhat do you need?




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Climate Change Annual Greenhouse Gas Index Noaa Climate Gov
The greenhouse effect on other planets Because the greenhouse effect is a natural process, it affects other bodies in the solar system, too And, in some cases, that provides a warning about howThe greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of life Human action, however, has increased the presence ofCO2 and the Mechanism of the Greenhouse Effect < /TD> A popular magazine recently publicized a journal article announcing that the Arctic had warmed much more than the rest of the Earth The reaction of amost anyone knowledgeable about the mechanisms of global warming is "Of course!" Here is an explanation of those mechanisms




Climate Change Evidence And Causes Royal Society




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
The answer lies in the greenhouse effect — gases in our atmosphere (including CO 2, CH 4 (methane) and H 2 O water vapor) trap much of the emitted heat and then reradiate it back to Earth's surface This means that the energy leaving our planet from the top of the atmosphere is less than one would expect given the known temperature of our planet



The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic
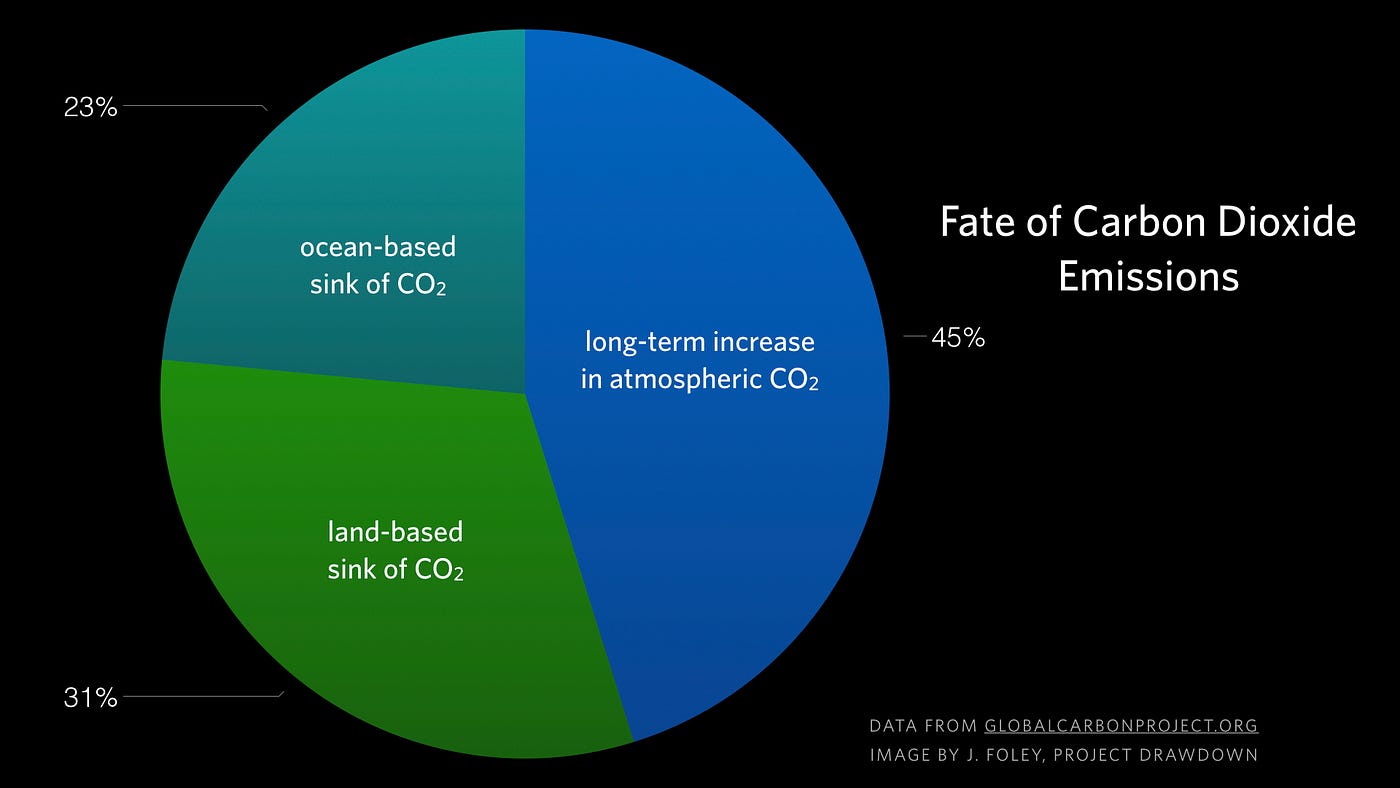



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Graphic Vector Illustration Greenhouse Effect Ozone Layer Illustration Ozone Layer Project
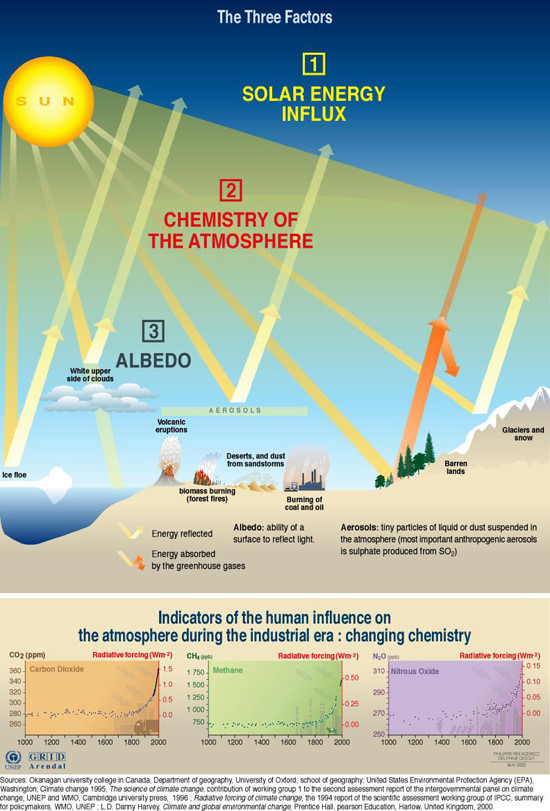



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal
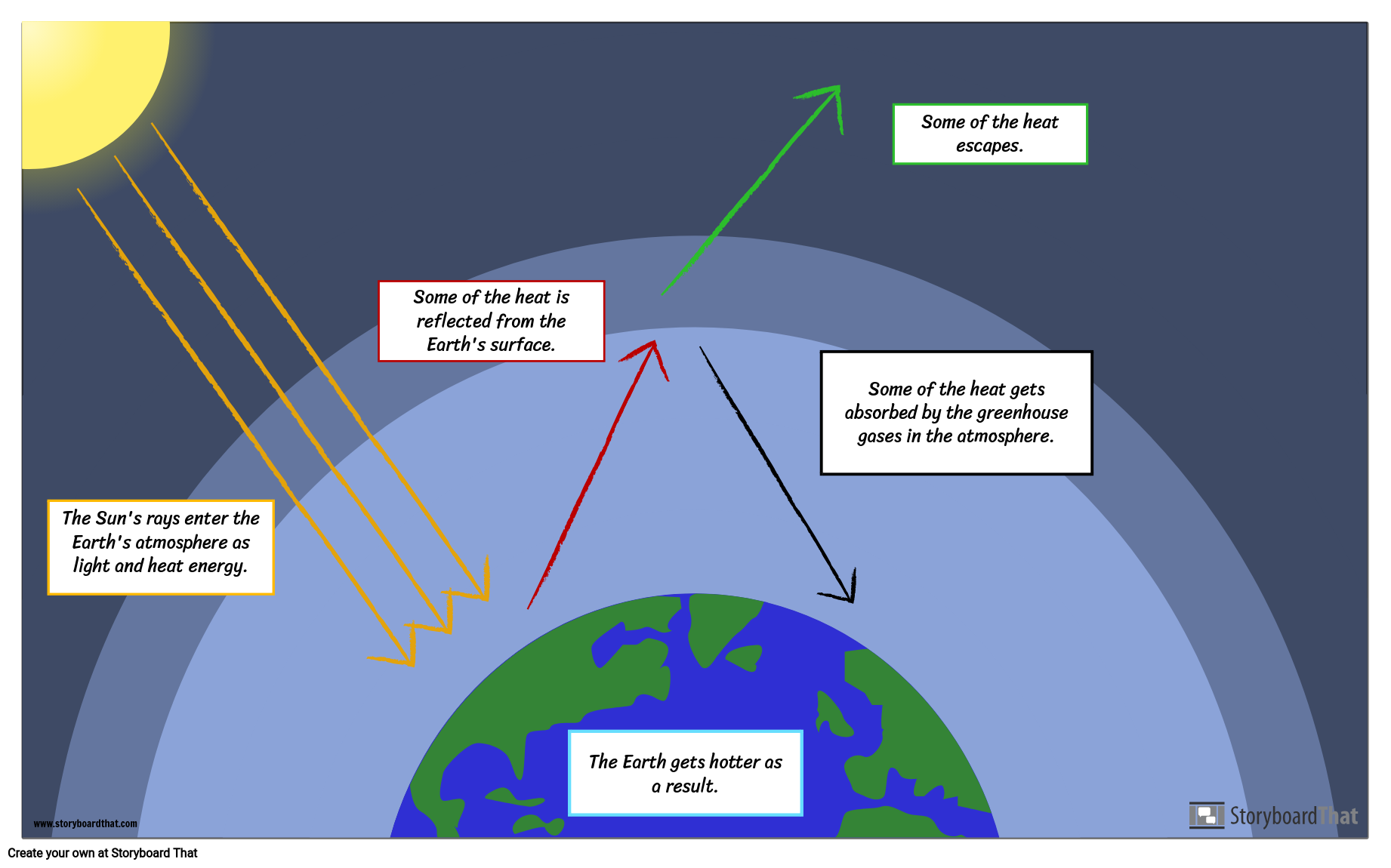



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




Understanding The Greenhouse Effect Sciencemusicvideos




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature



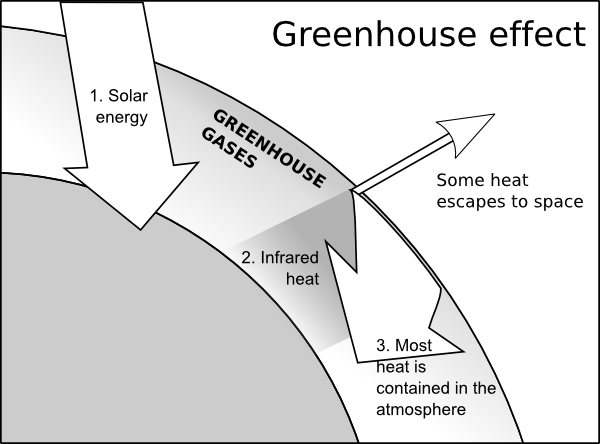
Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Diagram Quizlet




Greenhouse Effect Teaching Box Ucar Center For Science Education



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




The Greenhouse Effect Easily Understood With A Diagram Help Save Nature




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



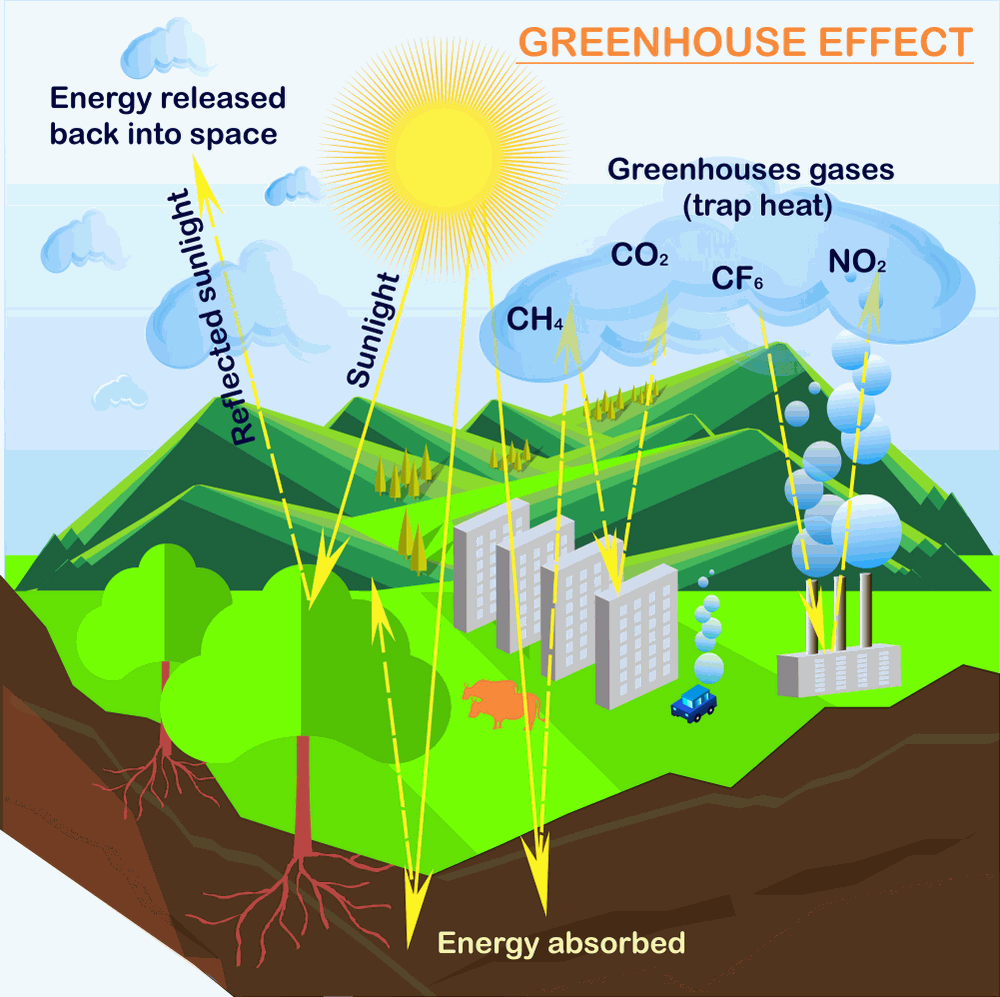
Top Of Greenhouse Effect Diagram Black And White Annejeannne




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Simple Climate




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey



Q Tbn And9gctoyncs8qyvzsnlf0ehywfdbiqsqkgodl5exlpxd0mjwanu7ugb Usqp Cau



1



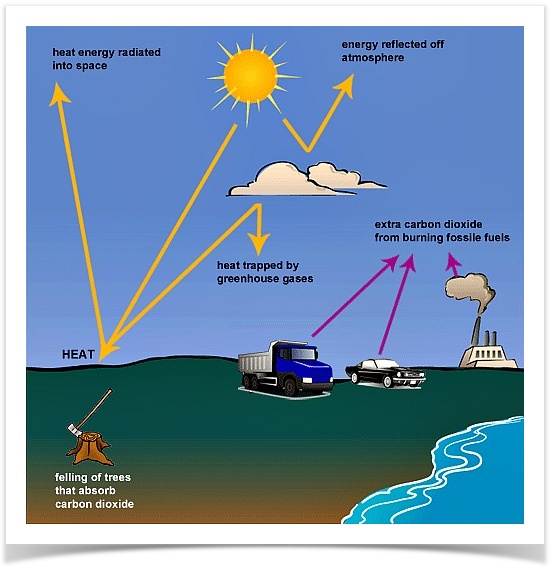
What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19



Graph Writing 162 Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan



Introduction To Greenhouse Gases Industry And Climate Change



Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustration Illustration Of Global




Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 154 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime



Chapter 7 The Greenhouse Effect




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Effect



What Is Climate Change Golden Gate National Recreation Area U S National Park Service




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Showing How The Greenhouse Effect Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering
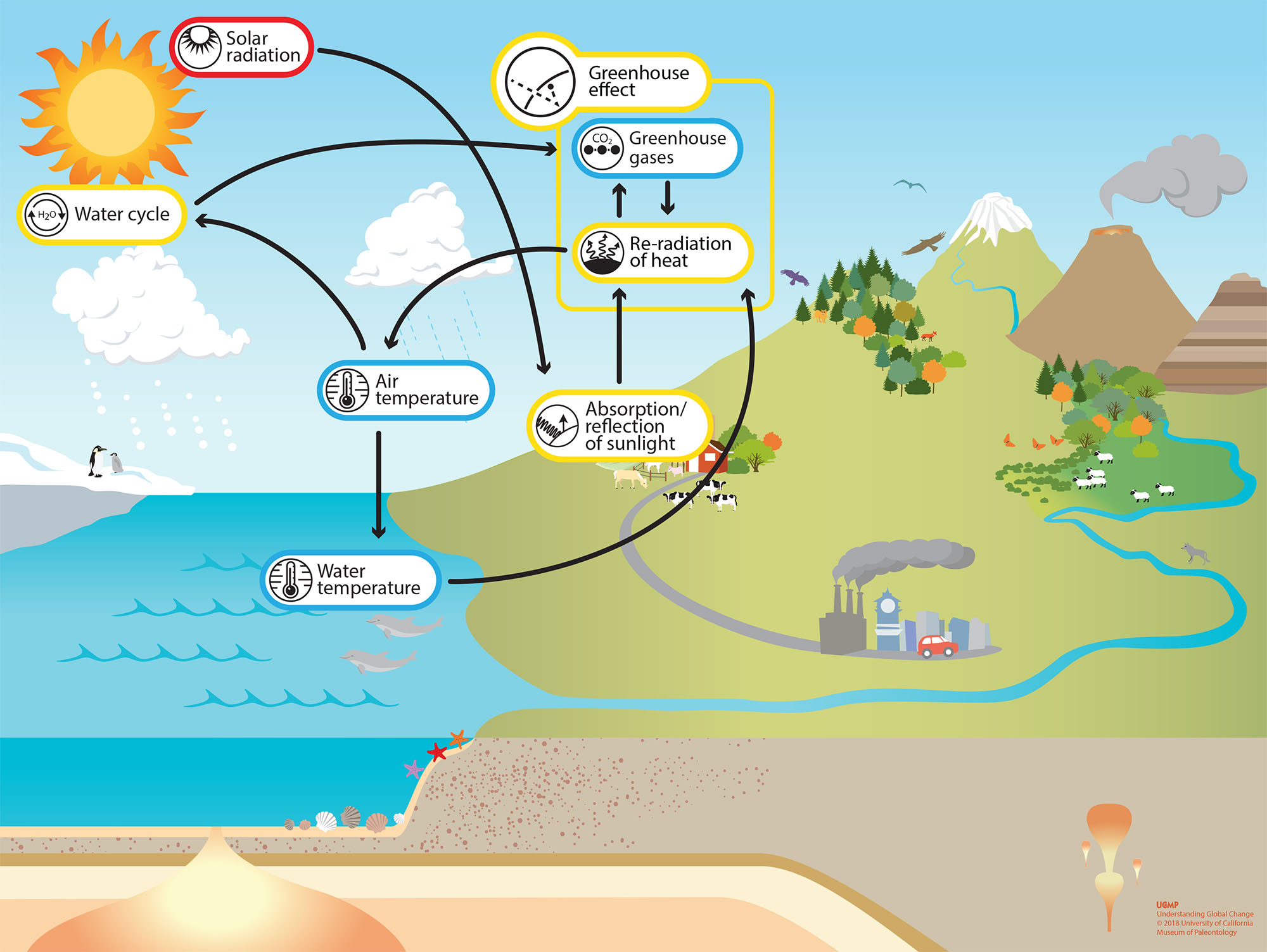



Greenhouse Effect Understanding Global Change




The Greenhouse Effect World101
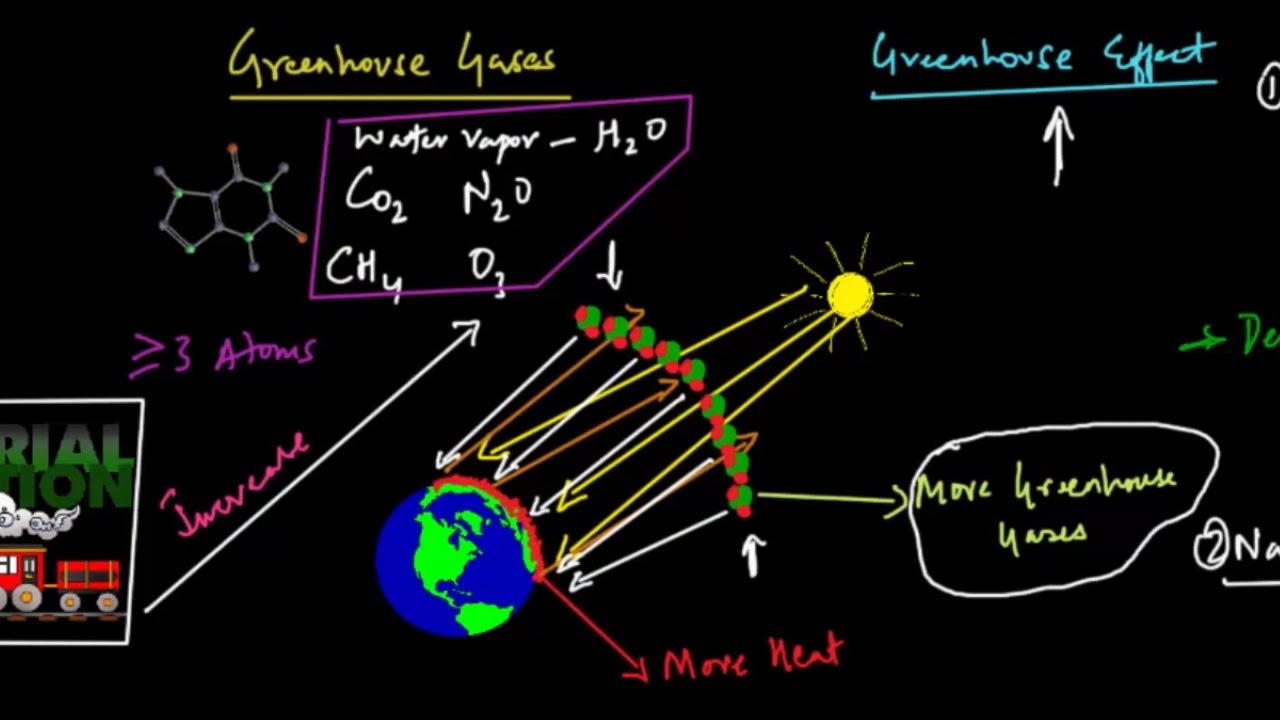



Understanding Greenhouse Gases And Greenhouse Effect Youtube



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change
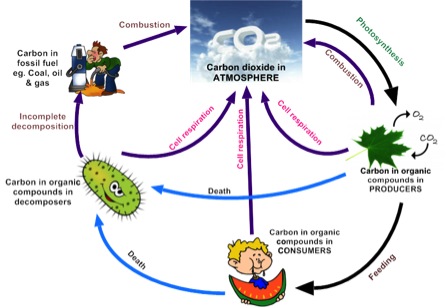



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp
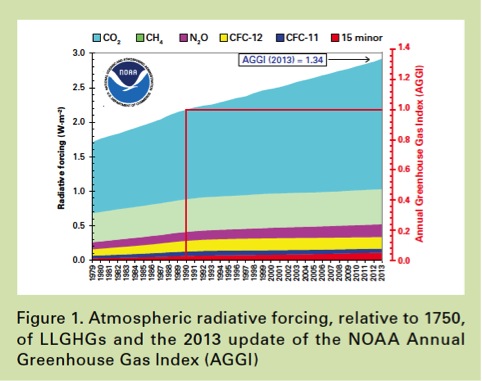



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Biology4ibdp




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids



Greenhouse Effect Diagram




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
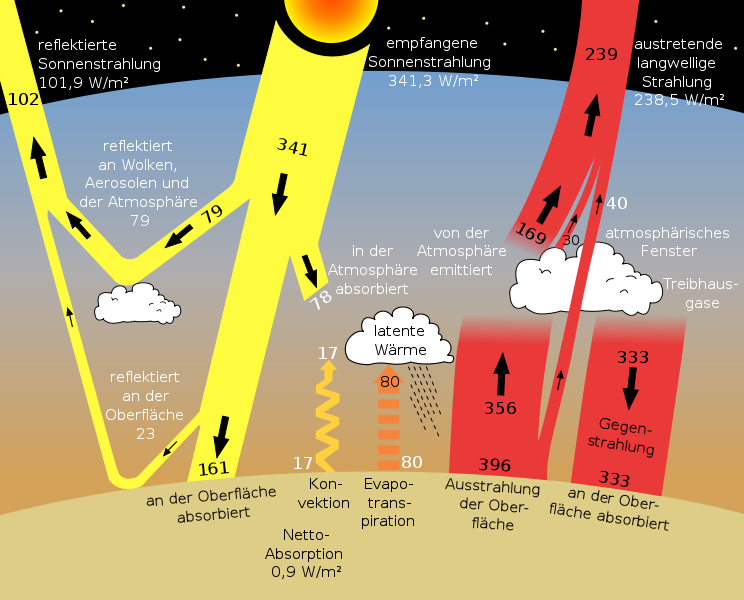



Greenhouse Effect Sankey Diagrams




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




629 Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Photos Pictures Royalty Free Images Istock



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Global Warming Lesson Plan



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube




Greenhouse Effect Diagram High Res Stock Images Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Scheme Diagram Showing How Stock Vector Royalty Free
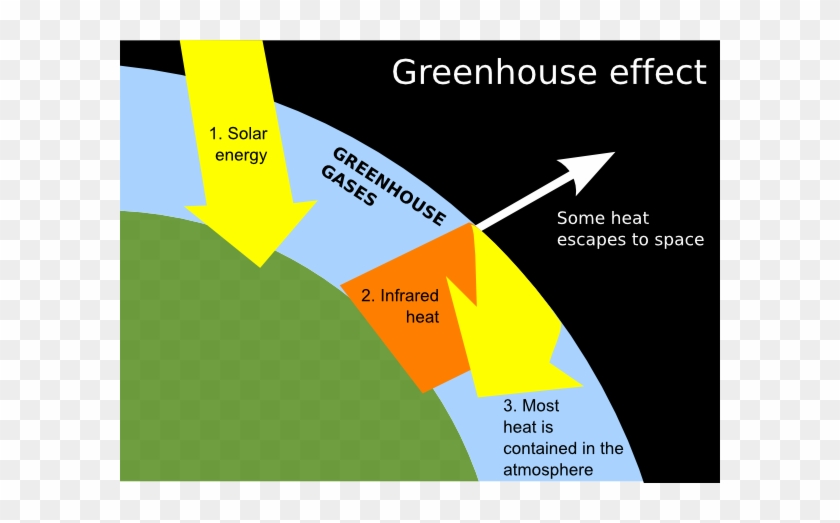



Greenhouse Clip Art At Clker Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download




Diagram Of The Greenhouse Gas Effect Download Scientific Diagram
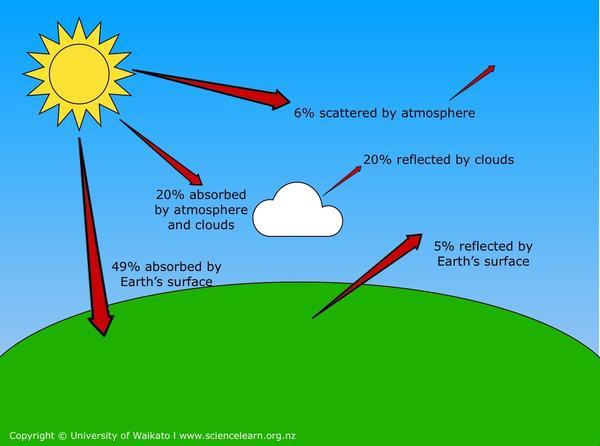



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿